
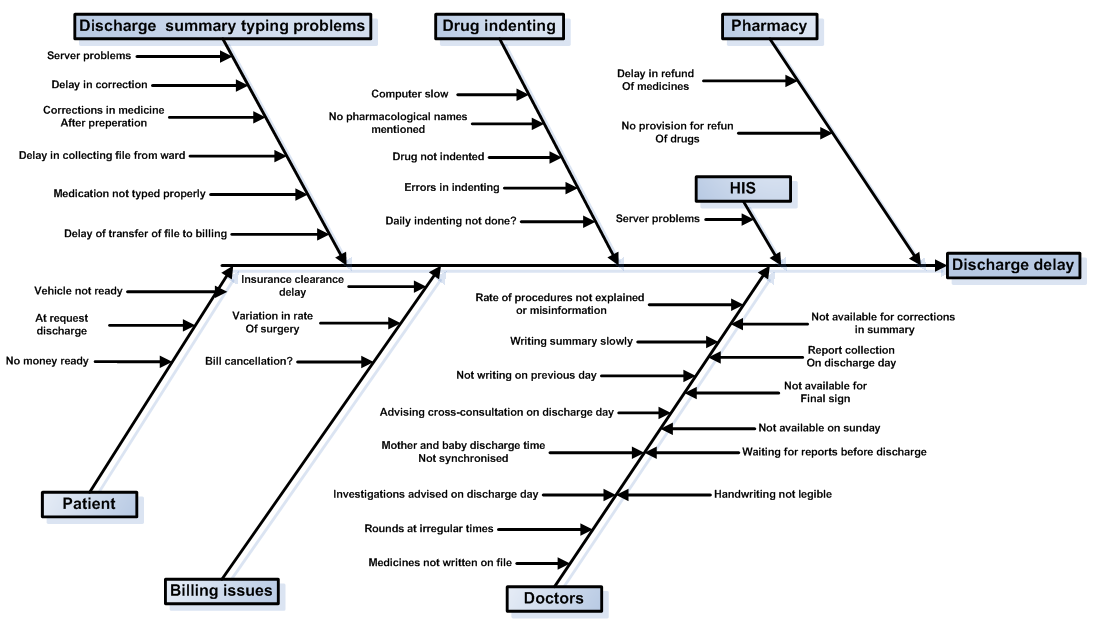
Step 9: Analyse the diagram and remove the causes keeping in Levels of causes if possible, and continue organizing them under related causes Step 8: Keep on identifying increasingly more detailed
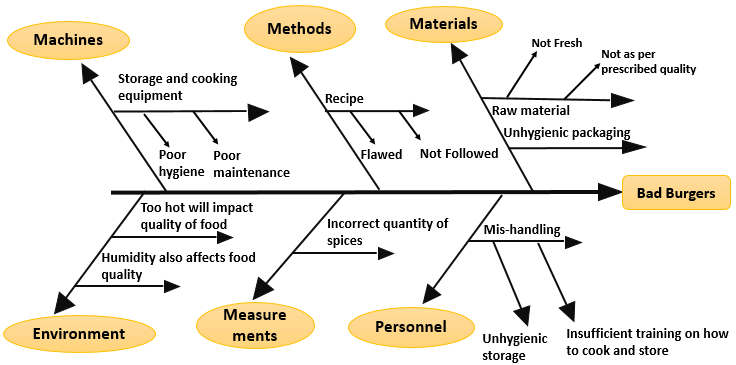
Step 7: For each primary cause, identify all possible Manufacturing is affected by temperature, humidity, dust and dirt, power Measurement instruments are adequate for the process? Are they maintainedĬorrectly and regularly calibrated? Are the measurement instruments affected byĮnvironmental conditions such as temperature, vibration, dirt, etc.? Varies with different suppliers? What types of material problems could exist? Material used in the process? Is there more than one supplier and does the quality There regular routine maintenance and preventative maintenance tasks? Are theyĬorrect materials are available for the process? What is the quality of the Machine have the ability to produce the product on a consistent basis? Are Machines have the capability to produce the product as specified? Does the Perform the task? Are the proper techniques available? Are the process Instructions are available and up-to-date? Do they reflect the best method to The operators have the proper training, experience, and ability to perform the Step 6: Identify all possible primary causes, in eachĬategory, contributing to the problem or effect being studied. The Processes: Process 1, Process 2, Process 3 and so on.The 4 Ss: Surroundings, Suppliers, Systems, Skills (recommended for service industries).The 8 Ps: Price, Promotion, People, Processes, Place / Plant, Policies, Procedures & Product (recommended for administration and service industries).The 6 Ms: Machine, Method, Materials, Measurement, Manpower and Mother Nature (Environment) (recommended for manufacturing industry).Causes in a cause & effect diagram are frequently arranged into the followingcategories: Step 5: Add main categories of possible causes of the problem.

Step 4: Draw a box containing the problem or effect to beanalysed, on the right side of the board with a horizontal spine. Step 3: Place a white board or flipchart where everyonecould clearly see it. A symptom differs from a problem in that the symptom is an evidence ofthe existence of a problem Identifying a very clearly defined andspecific problem is the first critical step to successfully implementing any problem-solving process. A problem exists when there is adifference between what "should be" and what "is" betweenthe ideal and the actual situation. A problem can be defined as a discrepancy betweenexisting and a desired state of affairs. Step 2: Identify, clearly state and agree on the effect orthe problem to be analysed. Gathering a teamof 4-7 individuals is recommended. It is recommended to form a team for "brainstorming". Step 1: Arrange a brainstorming session with the process team. Steps in Creating a Cause & Effect Diagram To analyze existing problems so that corrective action can be taken.To sort out and relate some of the interactions among the factors affecting a particular process or effect.To identify the possible causes or the basic reasons, for a specific effect, problem, or condition.Use cause & effect diagram when you want: It indicates possible causes ofvariation in a process and identifies areas where data should be collected forfurther study.

Ituses an orderly, easy-to-read format to diagram cause-and-effect relationships.It increases knowledge of the process by helping everyone to learn more aboutthe factors at work and how they relate. Itencourages group participation and utilizes team knowledge of the process. Hefirst used this diagram in 1943 at Kawasaki Steel Works.Ī cause & effect diagram helps to determine the causesof a problem or quality characteristic using a structured approach. Kaoru Ishikawa (1915-1989), a Japanese consultant, and fatherof the scientific analysis of causes of problems in industrial processes. It is also known as Ishikawa diagram because it wasinvented by Dr. It is also calleda fishbone diagram because the design of the diagram looks much like theskeleton of a fish. Because of its function of relating causes to theireffect, it is referred to as a cause-and-effect diagram. It can also be used to graphicallyillustrate the relationship between a given outcome and all the factors thatinfluence the outcome. A cause & effect diagram is a simple but very effectivetool that helps to identify, sort, and display potential or real causes of aspecific problem or quality characteristic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
